Radiometry
- Measurement system and units for illumination
- Accurately measure the spatial properties of light: Radiant flux, intensity, irradiance, radiance
- Perform lighting calculations in a physically correct manner
is the unit
Radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic radiation. It is measured in units of joules, and denoted by the symbol:
Radiant flux (power) is the energy emitted, reflected, transmitted or received, per unit time.
Radiant (Luminous) intensity is the power per unit solid angle(立体角) emitted by a point light source.
The candela is one of the seven SI base units.
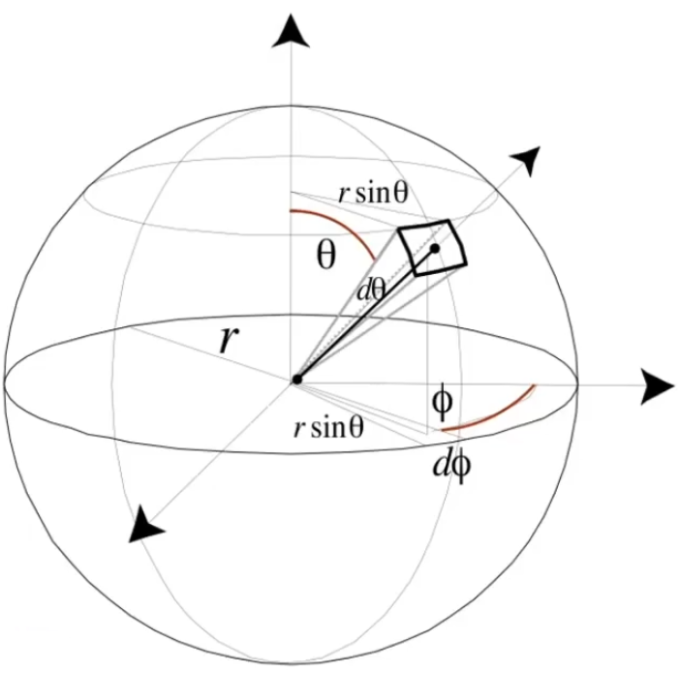
Angle: ratio of subtended arc length on circle to radius
, Circle has radians. is the arc length, is the radius. Solid angle: ratio of subtended area on sphere to radius squared
. Sphere has steradians. is the area on sphere, is the radius. Differential Solid Angles
Sphere:
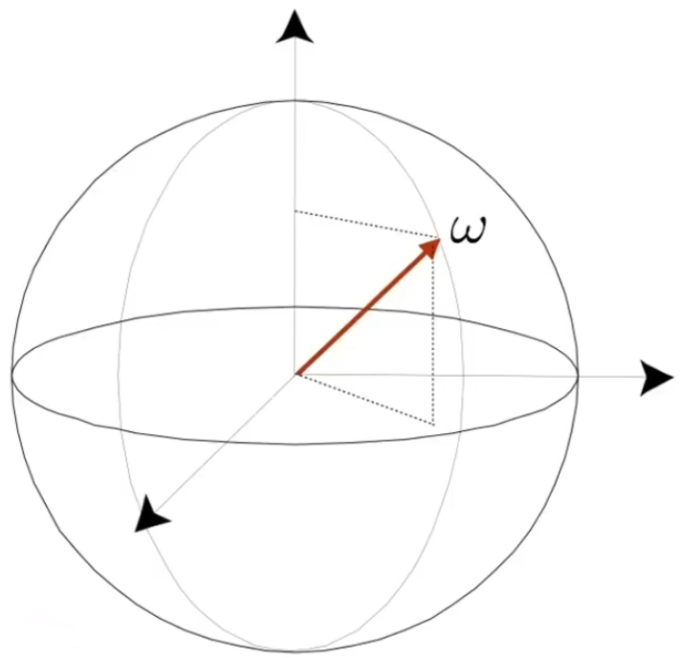
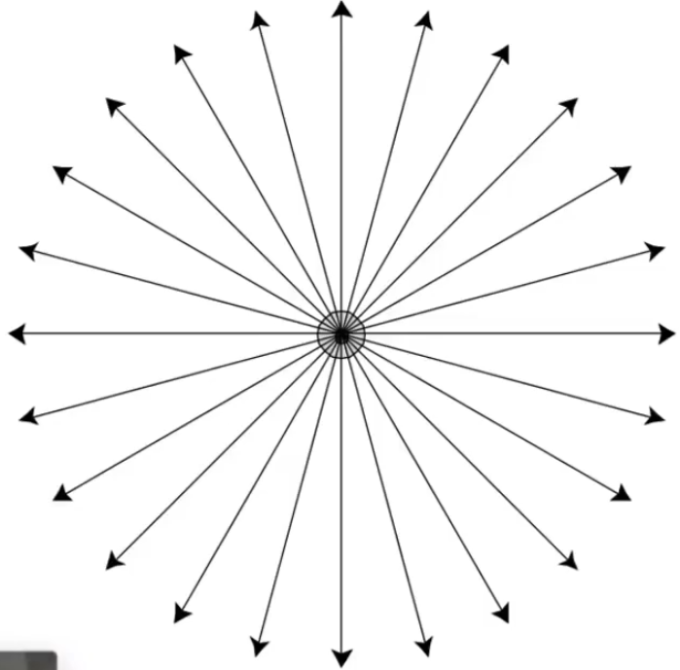
as a direction vector (unit length) Isotropic Point Source:
,
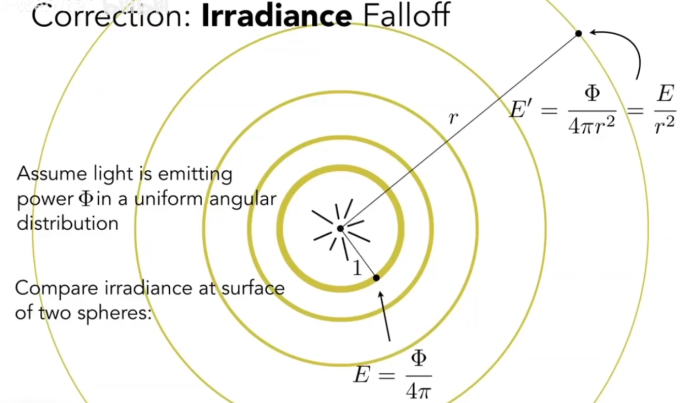
Irradiance is the power per (perpendicular/projected) unit area incident on a surface point.
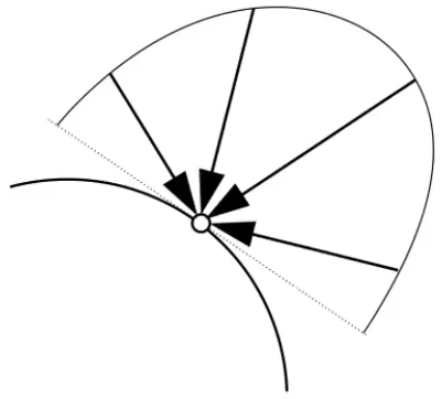
Irradiance at surface is proportional to cosine of angle between light direction and surface normal.
Radiance is the fundamental field quantity that describes the distribution of light in an environment. Radiance is the quantity associated with a ray. Rendering is all about computing radiance.
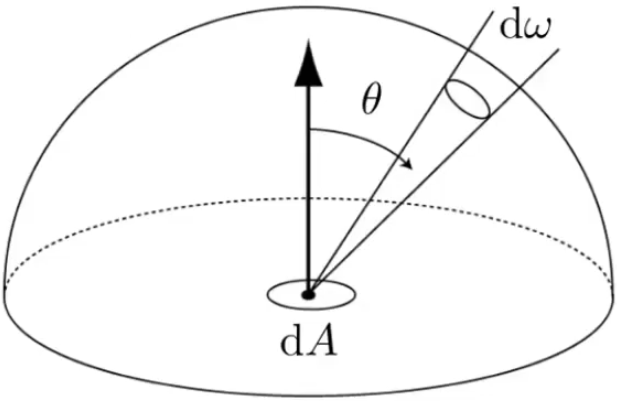
The radiance (luminance) is the power emitted reflected, transmitted or received by a surface, per unit solid angle, per projected unit area.

accounts for projected surface area.
Incident radiance is the irradiance per unit solid angle arriving at the surface.
Exiting surface radiance is the intensity per unit projected area leaving the surface.
Irradiance vs. Radiance
Irradiance: total power received by area dA
Radiance: power received by area dA from "direction"
Unit Hemisphere:
Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF)
Reflection at a Point: Radiance from direction
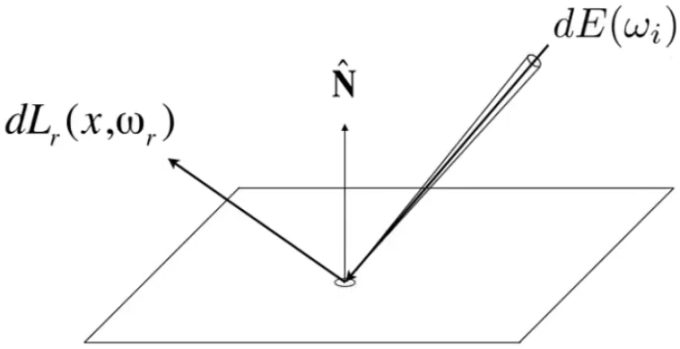
Differential irradiance incoming:
Differential radiance exiting (due to
BRDF: The Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function (BRDF) represents how much light is reflected into each outgoing direction
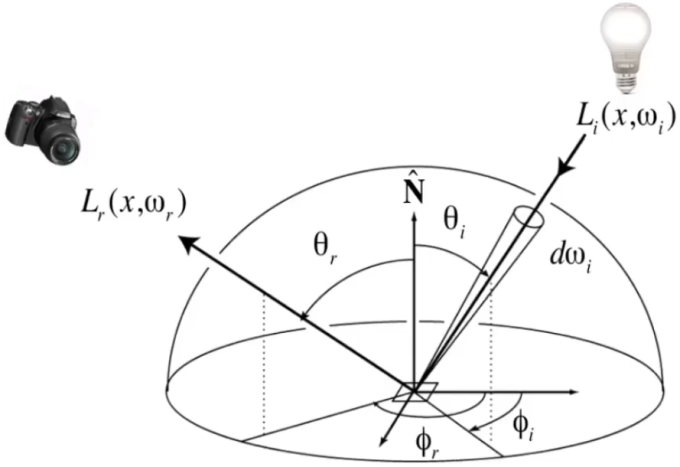
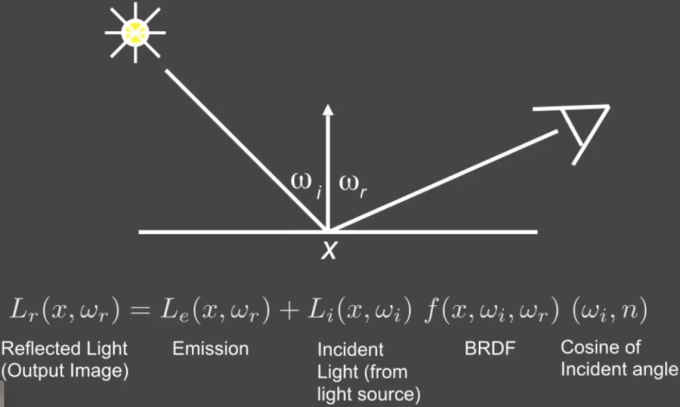
The Reflection Equation:
The Rendering Equation: Re-write the reflection equation by adding an Emission term to make it general.
assume that all directions are pointing outwards
Understanding the rendering equation:
Reflection Equation
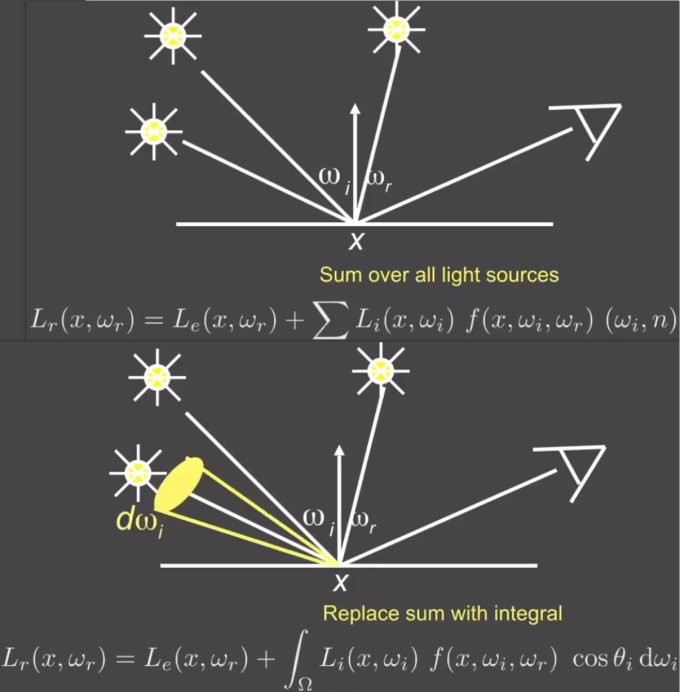
Rendering Equation
Rendering Equation as Integral Equation
Is a Fredholm Integral Equation of second kind [extensively studied numerically] with canonical form.
is the Kernel of equation Linear Operator Equation
Can be discretized to a simple matrix equation [or system of simultaneous linear equations] (L, E are vectors, K is the light transport matrix)
- Binomial Theorem
Ray Tracing:
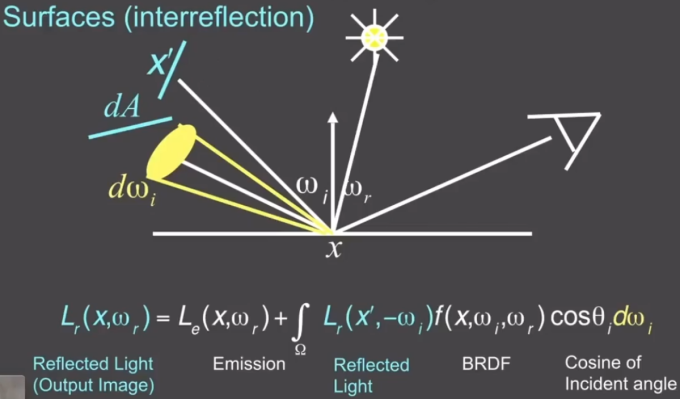
: Emission directly From light sources : Direct illumination on surfaces The following belong to Global illumination
: Indirect illumination (One bounce indirect) [Mirrors, Refraction] : Two bounce indirect illumination ...