Diffuse / Lambertian Material: Light is equally reflected in each output direction. Suppose the incident lighting is uniform
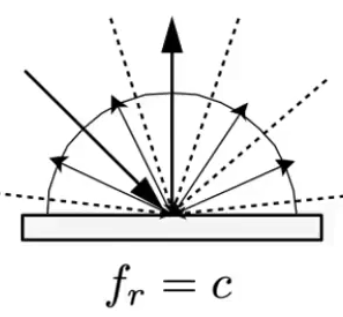
Suppose BRDF (
) is constant, incidence radiance ( ) is constant, incident radiance ( ) is equal to the exit radiance ( ).
Define a reflectance
Glossy Material (BRDF) 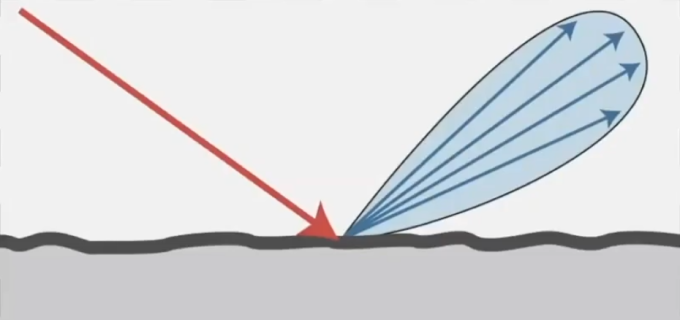
Ideal Reflective / Refractive Material (BSDF) 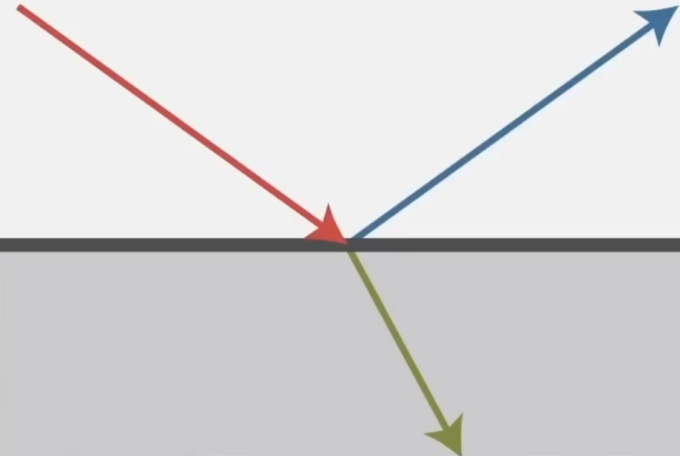
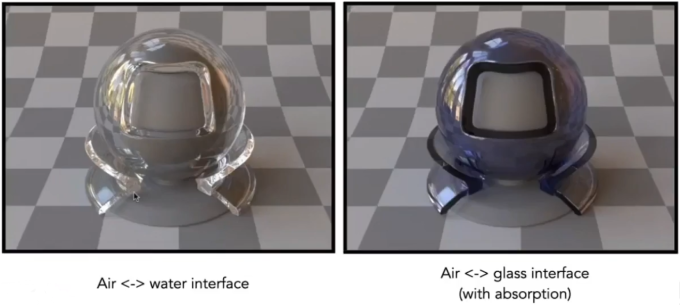
BSDF (Scatter) = BRDF (Reflection) + BTDF (Transmitted)
Perfect Specular Reflection
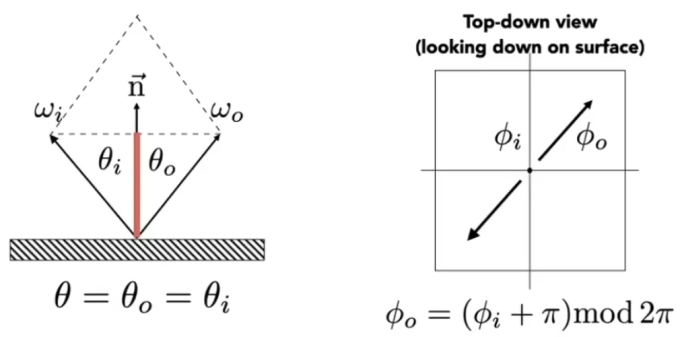
Specular Reflection: In addition to reflecting off surface, light may be transmitted through surface. Light refracts when it enters a new medium.
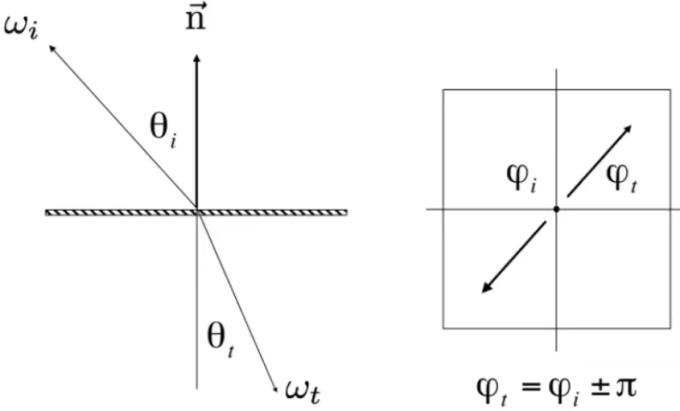
Snell's Law (Law of Refraction): Transmitted angle depends on
- index of refraction (IOR) for incident ray.
- index of refraction (IOR) for exiting ray.
: index of refraction is wavelength dependent (these are averages)
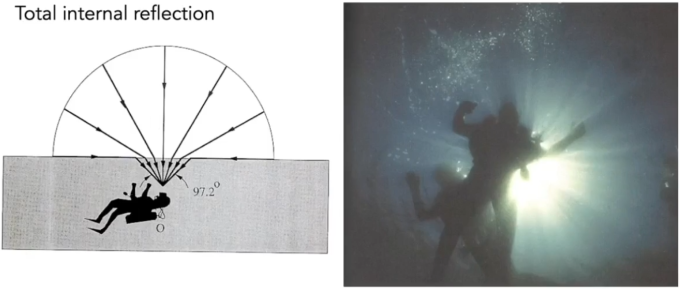
Total internal reflection:
When light is moving from a more optically dense medium to a less optically dense medium:
Light incident on boundary from large enough angle will not exit medium.
Snell's Window / Circle
Fresnel Reflection / Term: Reflectance depends on incident angle (and polarization of light)

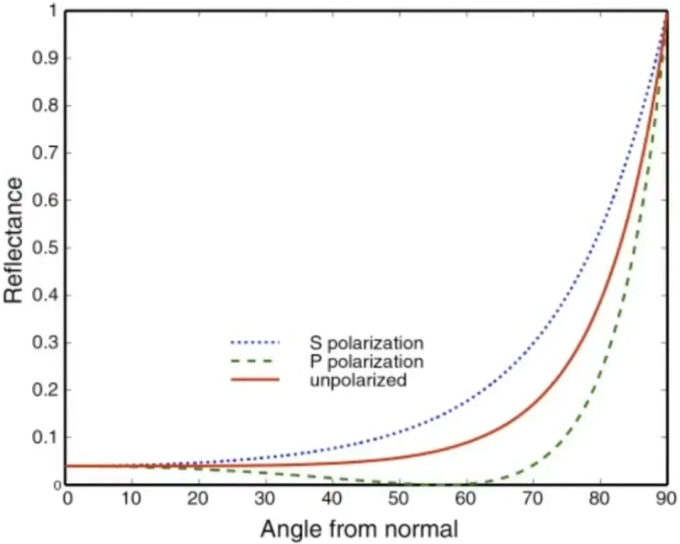
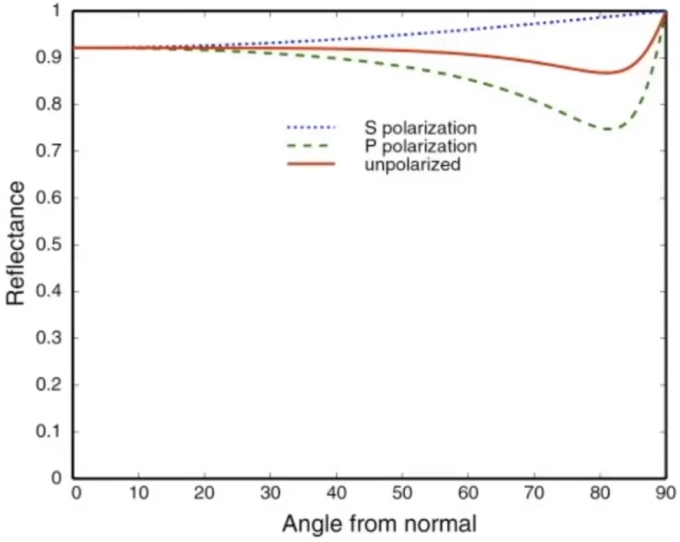
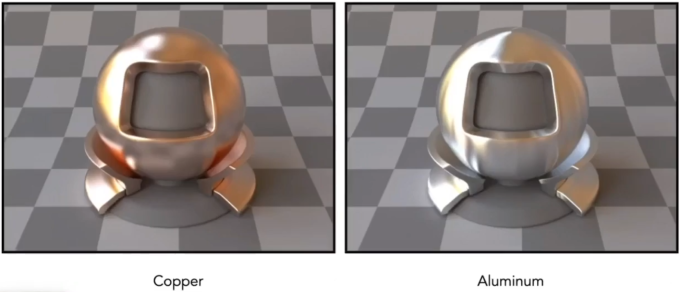
The left image is Dielectric (
), and the right image is Conductor.
Fresnel Term - Formulae:
- Accurate: need to consider polarization
- Approximate: Schlick's approximation
is
Microfacet Material 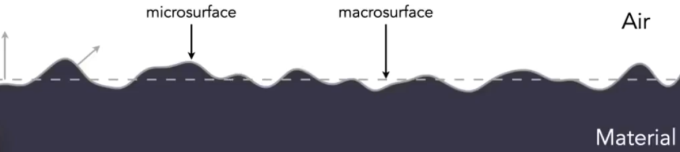
Rough surface
- Macroscale: flat & rough
- Microscale: bumpy & specular
Individual elements of surface act like mirrors
- Known as Microfacets
- Each microfacet has its own normal
Microfacet BRDF
Key: the distribution of microfacets' normals
Concentrated <==> glossy
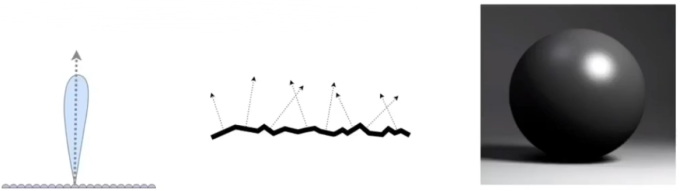
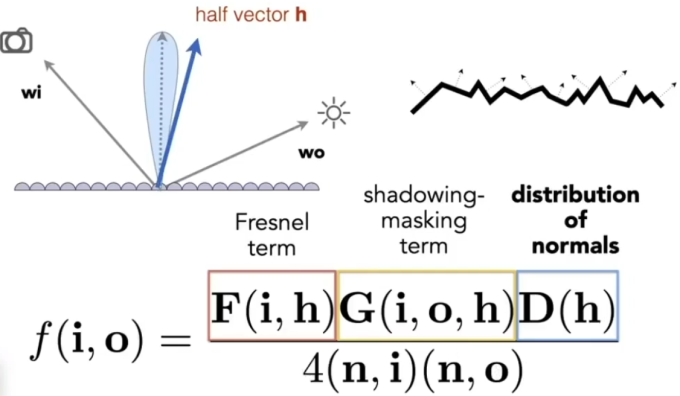
Spread <==> diffuse

Isotropic / Anisotropic Materials (BRDFs)
Key: directionality of underlying surface
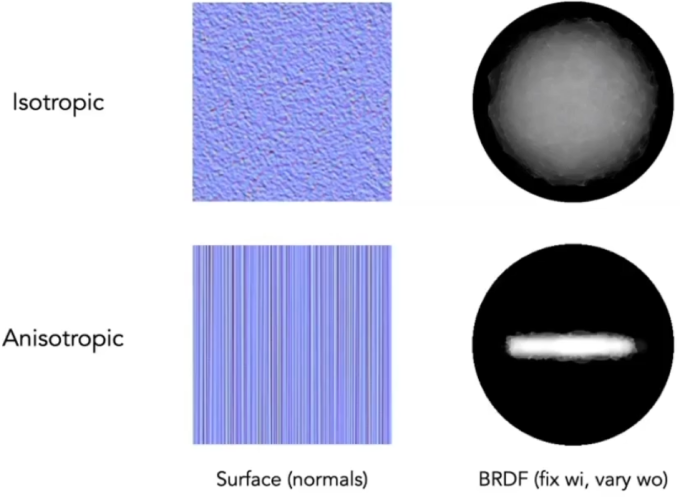
Anisotropic BRDFs: Reflection depends on azimuthal angle
, Results from oriented microstructure of surface, e.g., brushed metal, Nylon, Velvet
Properties of BRDFs
Non-negativity
Linearity
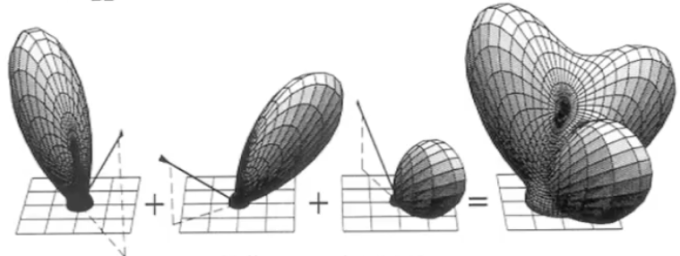
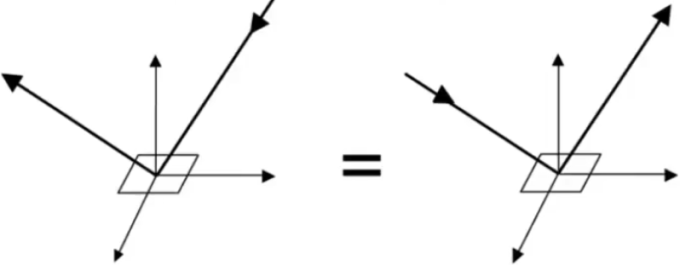
Reciprocity principle
Energy conservation
Isotropic vs. anisotropic
- If isotropic,
- Then, from reciprocity,
- If isotropic,
Measuring BRDFs
Image-Based BRDF Measurement: gonioreflectometer
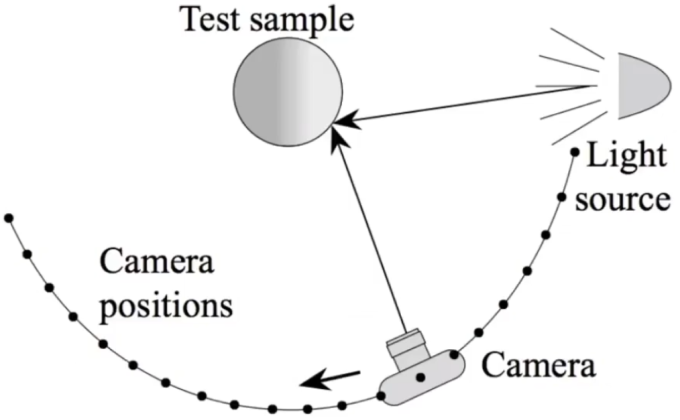
General approach:
for each outgoing direction wo move light to illuminate surface with a thin beam from wo for each incoming direction wi move sensor to be at direction wi from surface measure incident radianceImproving efficiency:
- Isotropic surfaces reduce dimensionality from 4D to 3D
- Reciprocity reduces # of measurements by half
- Clever optical systems...